Native Authentication Support
Currently, PubNub does not offer an authentication API solution (only Authorization).
To apply authentication logic to ChatEngine, one must update the [PubNub CE Function's](pubnubFunctions.md#PubNub CE Function) authPolicy() function to authenticate via a 3rd-Party provider such as GitHub, Facebook, Google, etc.
How to Support 3rd-Party Authentication
Basic Authentication via 3rd Party
Often, developers would prefer only known/validated users join ChatEngine Chat Rooms. Chat Rooms with a layer of authentication of user identity. PubNub does not provide an authentication API endpoint, leaving authentication solution up to the developer. Both 3rd party and self-built authentication service APIs follow the same paradigm when used with ChatEngine.
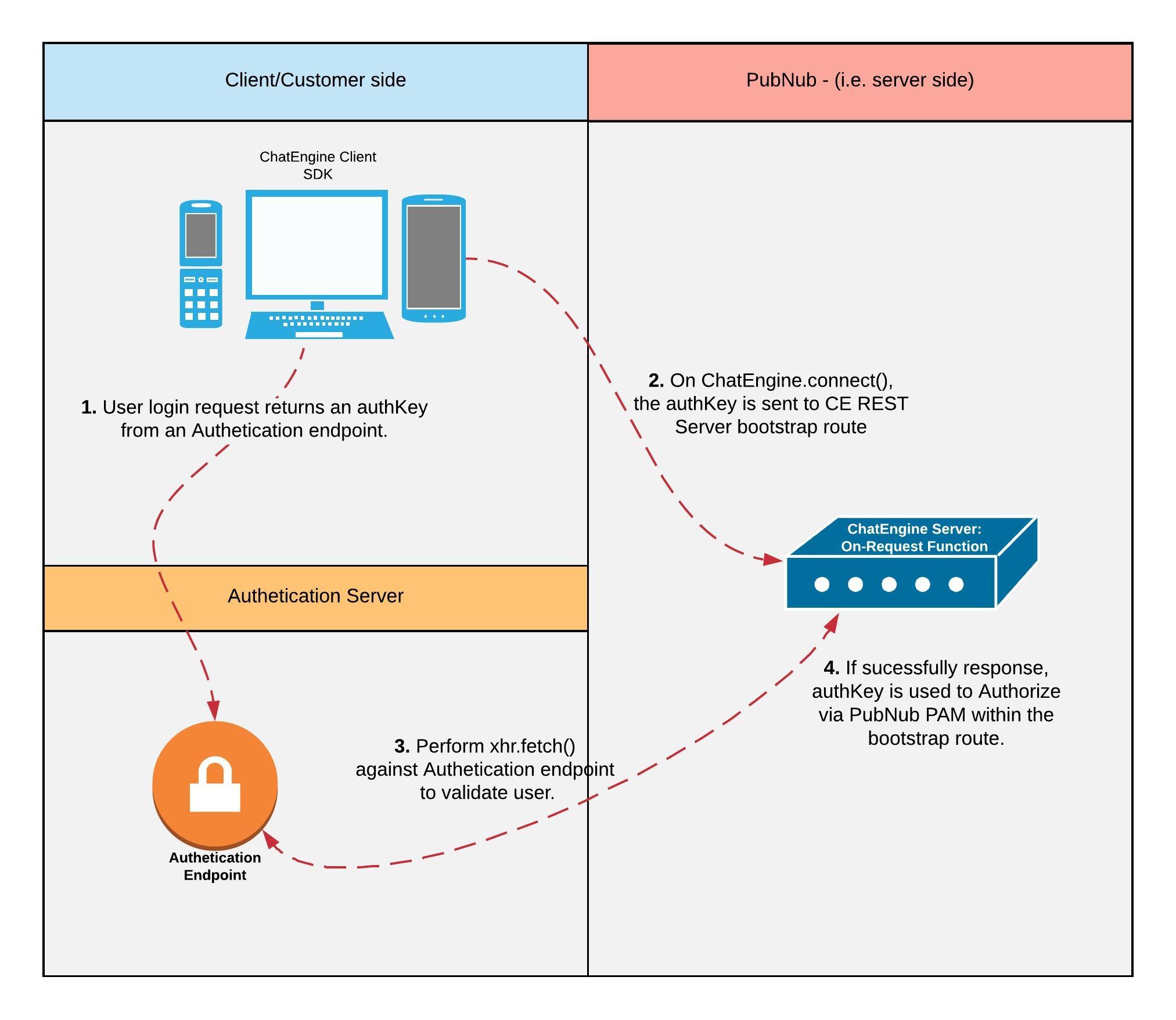
Main Steps
- Client initializes ChatEngine and includes a user/pass to some authentication endpoint.
- Authentication endpoint, if successful in validating the users's identity, passes an authentication token to the client.
- Client then passes the authentication token to the ChatEngine REST servers
bootstrapendpoint. - The Function REST endpoint, within the
src/functions/controllers/bootstrap.jsthen validates said user's identity against the 3rd party authentication endpoint. If successful, the bootstrap route will Authorize the user using the '''authKey''' argument to sign with PubNub's PAM. - They
authKey(Authentication token), returned to the client, is sent with every subsequent PubNub request (i.e. Publish/Subscribe) which is then validated via PAM. - Once the PAM ttl expires, the client will connect to the bootstrap route to begin to re-authenticate.
General Code Example
- Add an
authenticatecontroller to/src/functions/server.js. - Create
/src/functions/controllers/postAuthenticate.jswhich provides logic to communicate with 3rd party authentication server and allow access on successful identity validation. - Call the
postAuthenticate()route from thesrc/functions/controllers/postBootstrap.jsroute. - To bundle code, see Deploy Guide above (specifically the
gulp bundlestep).
1. Add controller.authenticate Route:
Open the following file /src/functions/server.js and add the lines below:
--- a/src/functions/server.js
+++ b/src/functions/server.js
--------------------------------
47 let controllers = {
48 + authenticate: {
49 + post: authenticatePost(request, response)
50 + },
51 bootstrap: {
52 post: bootstrapPost(request, response)
53 },
2. Create /src/functions/controllers/postAuthenticate.js:
--- a/src/functions/controllers/postAuthenticate.js
+++ b/src/functions/controllers/postAuthenticate.js
--------------------------------
import base64Codec from 'codec/base64';
import xhr from 'xhr';
const AUTHENTICATE_URL='https://fakeAuthApi/route/authenticate';
import validateAuthKey from '../validate/authKey';
export default (request, response) => {
// grants a user access to a new chat
return () => {
const authenticateUser = base64Codec.btoa(request.body.authenticateUser);
const authenticatePassword = base64Codec.btoa(request.body.authenticatePassword);
const authHeaders = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
};
const AUTHENTICATE_API_ENDPOINT = `${AUTHENTICATE_URL}?user=${autheticateUser}&password=${autheticatePassword}`
return xhr.fetch(`${AUTHENTICATE_API_ENDPOINT}`)
.then((res) => {
if (res.status_code === 200) {
response.status = 200;
return response.send({ 'authToken': res.authToken });
}
});
}
}
Strong Authorization
The ChatEngine server by default, authorizes anyone that joins to read/write on all ChatEngine Chat rooms. The authorization of users is handled by PubNub's PAM API. Theres a few code sections that should be updated in order to restrict access levels to the various Chat rooms.
Adding stricter PAM rules in these sections can add fine grain control of whether or not users get to: read, write, and or manage a Chat room (i.e. channel).
src/functions/controllers/invitePost.jssrc/functions/controllers/joinPost.jssrc/funcitons/controllers/leavePost.js
How one chooses to authorize is large up to the requirements of the Chat Room type. Is the room a private chat between a doctor and patient? Is the room a class of students and a teacher? The examples could go on, but the need to define access levels (ACLs) is imperative.
Inviting and Granting ACLs to New Users
The ChatEngine REST Function routes every request through an src/functions/authPolicy.js switch. The switch, by default, offers two authorization routes: invite|grant. By default, these return successful promise responses, and basically doing no authorization. Typically, these routes are where authorization should occur for inviting users to chat-rooms. Please use the Access Control API (i.e. PAM) to authorize users on the requisite chat-rooms.
Chat Room ACLs
Logic for these waterfall style connection handshakes can be in two places: src/functions/controllers/grantPost.js and src/functions/controllers/joinPost.js.